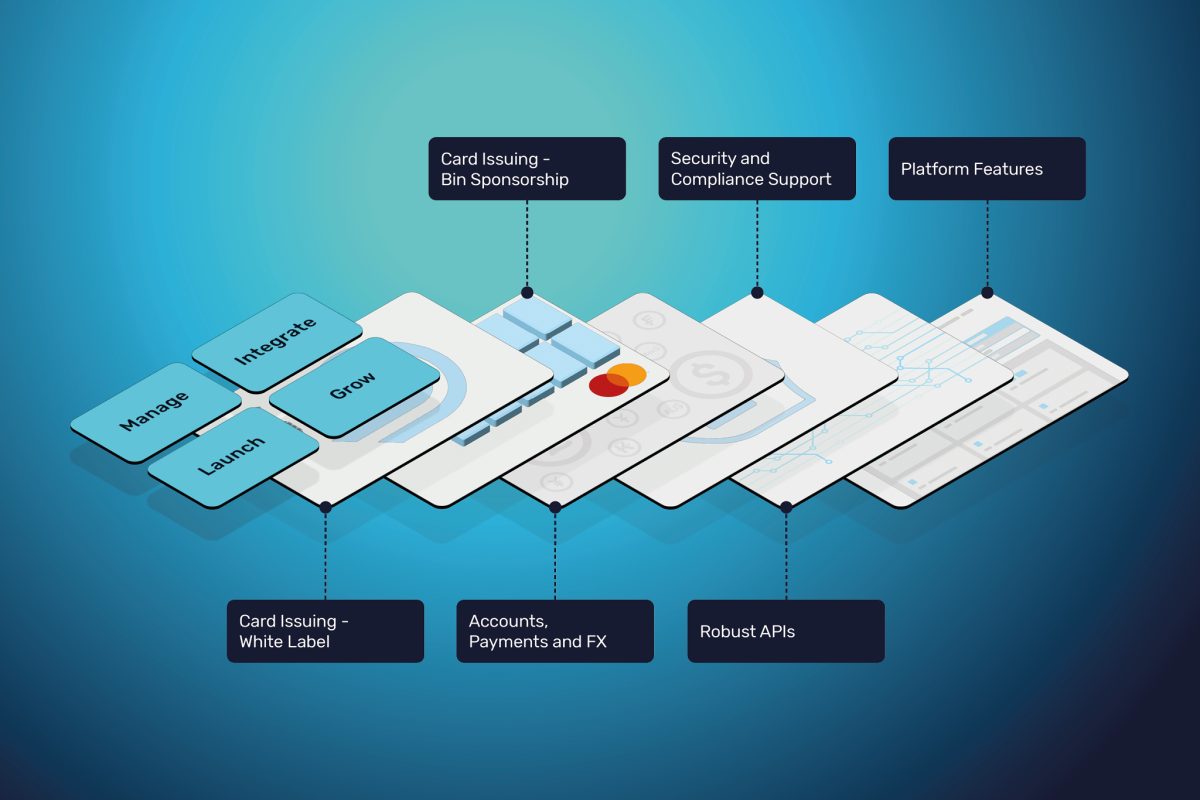
Innovation and digitisation continue to break down barriers, and the lines between traditional ways of serving customers are being redefined. Businesses are keen to ride this wave of change and enhance their services and customer experiences. Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) is one of the most compelling examples of how the tide is turning and delivering flexibility, efficiency, and heightened customer engagement.
In this blog, we dive into the basics of BaaS, explain why it’s captured the imagination of businesses worldwide and provide some key examples of BaaS in action.
What is BaaS?
Changes to financial services rules and regulations mean that banks have lost their monopoly on providing financial services. Today, you don’t need to be a bank to offer banking services. You just need to work with a service provider that adheres to strict regulations and has the proper permissions.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) is therefore a significant shift in the way banking functions are delivered and consumed. It enables businesses to integrate banking services directly into their own systems, making transactions and other banking activities more efficient and user-friendly.
BaaS operates on a digital infrastructure where a licensed financial services provider offers financial products or services on a modular basis to other businesses.
It removes the barrier to entry in the financial world by providing businesses with a framework they can use to offer banking services without having to build them from scratch, which would be a considerable investment of time and money.
The components of BaaS range from payments and deposits to lending and compliance services, all delivered through a digital interface. It allows non-bank organisations to integrate all financial components into their operations.
The adoption of BaaS solutions brings benefits such as reduced operational costs, improved customer experience, quicker time-to-market, and increased revenue streams.
How BaaS Works: Unravelling the Mechanics
BaaS operates primarily through API integrations.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are software intermediaries that allow different applications to communicate with each other.
In BaaS, APIs are used to link businesses’ systems with the services provided by banks or financial institutions. This enables businesses to offer modular banking solutions such as account creation, payments, or card issuance without the need for extensive banking infrastructure.
The Role of BIN Sponsorship
BIN Sponsorship plays a critical role in BaaS.
BIN stands for Bank Identification Number and is the first four to six numbers that appear on payment cards.
BIN Sponsorship allows non-bank entities to issue payment cards under their own brand. A BIN Sponsor is a bank or financial institution that is part of a card network and can facilitate payment card transactions.
By leveraging BIN Sponsorships, businesses can process seamless payments without having to directly interface with card networks or financial institutions.

BIN Sponsorships simplify regulatory compliance, as the sponsor bank handles all compliance-related matters, including anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures.
The Need for BaaS: Addressing 6 Key Challenges
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) addresses six key challenges that have been prevalent in traditional banking systems:
1. Access to Banking for Non-Banks
BaaS lowers the barriers to entry for non-banking businesses that want to offer financial services. Through partnerships with BaaS providers, companies that do not have a banking license can still offer their customers banking services.
2. Agility and Speed
Traditional banking systems are often characterised by their slow and cumbersome processes. BaaS, with its digital infrastructure, allows for much faster and more agile operations. The API integrations allow businesses to quickly implement banking services and adapt to market changes with minimal delay.
3. Customer Experience
The traditional banking experience is often less than ideal for customers, who now expect seamless and instant services. BaaS enhances the customer experience by integrating banking services directly into the platforms they already use, making banking more accessible and convenient.
4. Cost Reduction
Establishing and maintaining a traditional banking infrastructure is expensive. BaaS allows businesses to leverage the infrastructures of existing banks alongside the automation and digitisation of services which reduces operational costs.
5. Scalability
Traditional banking systems are not easily scalable. BaaS, with its modular approach, allows businesses to scale their operations efficiently. They can select and integrate the services they need, and easily add or remove services as their requirements change.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Complying with the complex regulatory requirements in banking is a significant challenge. BaaS providers often handle compliance, reducing the burden on businesses and ensuring that services are provided within the regulatory framework.
Key Examples of BaaS in Action
The implementation of BaaS has transformed various industries.
1. Fintech
In e-commerce, businesses use BaaS to simplify payments, making checkouts smoother and improving the overall shopping experience. In the gig economy, companies use BaaS to provide faster payouts to their workforce, enabling real-time payments.
2. eCommerce
In e-commerce, businesses use BaaS to simplify payments, making checkouts smoother and improving the overall shopping experience. In the gig economy, companies use BaaS to provide faster payouts to their workforce, enabling real-time payments.
3. Telecommunications
Telecom companies can enable their customers to perform transactions, such as mobile money transfers, paying bills, and purchasing airtime, seamlessly through their mobile phones. This integration is particularly beneficial in developing regions where banking infrastructure is limited, but mobile phone usage is widespread.
4. Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics can integrate BaaS solutions to enable easy and secure payment options, reducing administrative workload and enhancing the patient’s experience. Healthcare providers can leverage BaaS platforms to offer tailored financial products such as health savings accounts or payment plans.
5. Travel and Hospitality
Hotels and travel agencies can integrate BaaS to offer seamless booking and payment processes. They can create loyalty programs that reward customers with points that can be converted into financial benefits. This not only increases customer satisfaction but also builds brand loyalty.
Stay close to customers with BaaS
Banking-as-a-Service is more than just a solution for today’s banking challenges – it’s a forward-looking approach that’s set to redefine the financial landscape of tomorrow.
As businesses recognise the benefits of BaaS, from operational efficiency and agility to enhanced customer experiences, its adoption is only poised to grow.
In this new era of banking, the adoption of BaaS isn’t just an option; it’s a strategic necessity for businesses wanting to stay competitive and relevant.
With the added capability of providing real-time payments, personalised experiences, and facilitating digital transformation across sectors, BaaS unlocks a strategic advantage in an increasingly competitive market.
Embracing BaaS means embracing a future of seamless, customer-centric, and cost-effective banking solutions that work for the ever-evolving requirements of your business.